Table of contents
- 📍 Introduction:
- 📍 What is Ingress?
- 📍 Why Ingress, what problems have we faced with service load balancers?
- 📍 Comparison b/w VM based & K8's Service Load Balancers
- 📍 Load Balancer IP vs Ingress
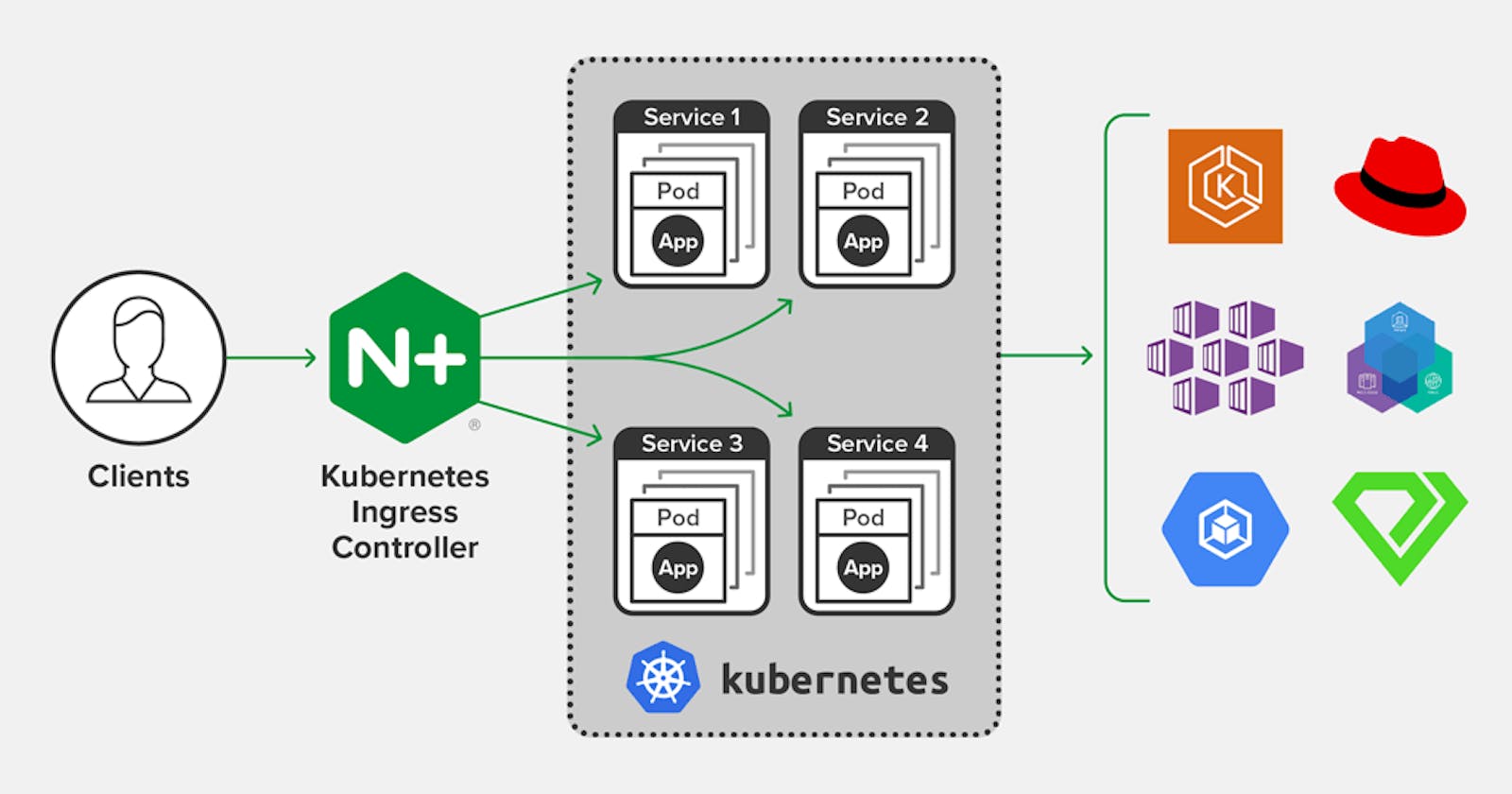
- 📍 What is Ingress Controller?
- 📍 Different types of Ingress Controllers
- 🔹 Here is an example of how to create an Nginx Ingress resource in Kubernetes:
- 📍 Conclusion:
- 🔹 Checkout GitHub Repository for projects:
📍 Introduction:
In a Kubernetes environment, there are many different ways to expose your application to the outside world. One of the most popular methods is through the use of a load balancer or an ingress controller. In this blog post, we will learn about what is ingress, its importance, the problems we faced with service load balancers, the difference between load balancer IP and Ingress, Ingress Controller, and the different types of Ingress Controllers.
📍 What is Ingress?
Ingress is a Kubernetes resource that provides a way to expose HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. It acts as a reverse proxy, routing incoming traffic to the appropriate service based on the URL path and host specified in the request. In simpler terms, Ingress provides a way to manage external access to your services in a more intelligent and flexible way than a simple load balancer.
📍 Why Ingress, what problems have we faced with service load balancers?
Service Load Balancers in Kubernetes are used to distribute incoming traffic across multiple replicas of a service. However, Service Load Balancers have some limitations, such as:
Lack of flexibility: Service Load Balancers only support simple HTTP routing based on the service's IP address and port number. In contrast, Ingress can route traffic based on host names, URL paths, and more.
Limited SSL/TLS support: Service Load Balancers do not provide built-in SSL/TLS termination, which means you need to set up SSL/TLS termination yourself, which can be complex.
Limited scalability: Service Load Balancers are typically limited to a single IP address per service, which can limit the number of services that can be exposed externally.
In contrast, Ingress provides a more flexible, scalable, and feature-rich way of exposing services externally.
📍 Comparison b/w VM based & K8's Service Load Balancers
Virtual Machine-Based Enterprise-level Load Balancers:
Pros:
Highly customizable and feature-rich
Can handle large-scale traffic and complex configurations
Offer advanced security features such as DDoS protection and SSL offloading
Can be used for both on-premises and cloud-based environments
Cons:
Expensive to purchase and maintain
Requires specialized expertise to manage and configure
Scaling up requires additional hardware and resources
Lack of portability between different environments
Service Load Balancers of Kubernetes:
Pros:
Native to Kubernetes and easy to deploy
Automatic load balancing for services within a cluster
Cost-effective and scalable
Supports multiple load-balancing algorithms
Integrates with other Kubernetes features like DNS and IP address management
Cons:
Limited to managing traffic within the Kubernetes cluster
May not have all the advanced features of virtual machine-based load balancers
Relies on the underlying cloud provider's load-balancing infrastructure
May not handle large-scale traffic as well as virtual machine-based load balancers
It's important to note that the choice between virtual machine-based enterprise-level load balancers and service load balancers of Kubernetes depends on the specific needs and requirements of your application and infrastructure.
📍 Load Balancer IP vs Ingress
When exposing your application to the outside world, you have two options: a load balancer IP or an Ingress. A load balancer IP is a service that exposes your application to the outside world using a static IP address. It can be used to distribute traffic to multiple pods or services.
On the other hand, an Ingress is a resource that provides a way to expose HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. It can route traffic based on the URL path or hostname, making it more flexible than a load balancer IP.
📍 What is Ingress Controller?
An Ingress Controller is a Kubernetes resource that runs as a pod in the cluster and is responsible for implementing the rules defined in Ingress resources. In other words, the Ingress Controller is the component that handles the traffic routing based on the Ingress rules.
There are many different Ingress Controllers available for Kubernetes, each with its unique features and limitations. Some of the most popular Ingress Controllers include:
Nginx Ingress Controller: a popular open-source Ingress Controller that supports advanced traffic routing features such as SSL/TLS termination, rewrite rules, and more.
Traefik: a popular open-source Ingress Controller that supports advanced features such as automatic Let's Encrypt SSL certificate provisioning, middleware, and more.
Istio: a service mesh that includes an Ingress Controller that supports advanced traffic routing features such as traffic splitting, canary deployments, and more.
📍 Different types of Ingress Controllers
There are different types of Ingress Controllers that you can choose from, depending on your needs. Some of the most popular ones are:
Host-based routing: With this type of routing, traffic is routed based on the hostname specified in the request URL. For example, you can route traffic for
app1.example.comto one service and traffic forapp2.example.comto another service.Path-based routing: With this type of routing, traffic is routed based on the URL path specified in the request URL. For example, you can route traffic for
/API/v1to one service and traffic for/webto another service.TLS termination: This type of Ingress Controller handles SSL/TLS termination for incoming traffic. It allows you to use HTTPS with your services without having to set up SSL/TLS termination manually.
Custom routing: Some Ingress Controllers allow you to define custom routing rules using middleware. Middleware allows you to add additional functionality to your Ingress rules, such as rewriting URLs or modifying headers.
🔹 Here is an example of how to create an Nginx Ingress resource in Kubernetes:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- host: example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /api
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: api-service
port:
name: http
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: web-service
port:
name: http
- This Ingress resource will route traffic for
example.com/apito theapi-serviceand traffic forexample.comto theweb-service. It also includes an annotation that enables URL rewriting for requests to theweb-service.
📍 Conclusion:
In summary, Ingress is a Kubernetes resource that provides a way to expose HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. It allows you to route traffic based on the URL path or hostname, making it more flexible than a service load balancer. Ingress Controllers are responsible for managing the Ingress resource and configuring the load balancer or proxy used to route traffic to the backend services. There are many different types of Ingress Controllers available, each with its own set of features and capabilities. Incorporating Ingress into your Kubernetes environment can greatly simplify the process of exposing your applications to the outside world. It provides a single point of entry for all HTTP and HTTPS traffic, making it easier to manage and configure.
While service load balancers have their own set of limitations, Ingress provides a more flexible and scalable solution. With the ability to route traffic based on the URL path or hostname, it allows for more granular control over the traffic flowing into your applications.
In addition, the availability of various Ingress Controllers provides the option to select the best one that fits your specific use case. This enables you to customize the Ingress Controller to better suit your application requirements and leverage additional features that the controller offers. To sum up, Ingress is an essential tool in managing your Kubernetes environment. It provides a powerful and flexible way to route traffic to your applications, and with the many Ingress Controller options available, you can select the best one to fit your specific needs.
🔹 Checkout GitHub Repository for projects:
🔗 https://github.com/sumanprasad007